The UK government published the smart charging regulations, which came into force in June 2022. These regulations require all new private (domestic and workplace) charge points sold in Great Britain to have smart functionality. This includes charge points installed at homes, businesses, and other private premises. These charge points must send and receive information. They should also respond to signals to adjust the charging rate and, in addition, provide demand-side response services.
The industry reacted strongly to these regulations when they were first introduced. As a result, chargepoint manufacturers faced a tight deadline to comply. Nevertheless, the British government set a new global standard for chargepoint capabilities and security in the connected energy world.
Goals of the UK Smart Charging Regulations
The main goals of the UK smart charging regulations are to:
- Manage increasing electricity demand from the UK’s transition to electric vehicles (EVs)
- Improve security protocols
- Make charging more convenient and affordable for EV owners
Benefits of Smart Charging
The UK expects the regulations to play a key role in achieving its net zero emissions targets. Here are some specific examples of how smart charging, more than a year into play already, is helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the UK:
- A recent study by the Energy Systems Catapult found that smart charging could reduce the UK’s electricity carbon intensity by up to 10% by 2030.
- The National Grid has estimated that smart charging could save the UK up to 20 million tonnes of CO2 emissions per year by 2030.
Although the regulations caused temporary challenges for manufacturers, they represent a significant positive step towards Net Zero.
UK Smart Charging Regulations Phases
The UK smart charging regulations came in two phases:
Phase 1
Phase 1, which came into force on June 30, 2022, applies to all new charge points installed in the UK after that date. Specifically, it includes the following requirements:
- Smart functionality
- Electricity supplier interoperability
- Loss of communications network access
- Safety
- Measuring system
- Off-peak charging
- Randomised delay
- Assurance
- Register of sales
Phase 2
Phase 2, which came into force on December 30, 2022, applies to all new charge points installed in the UK after that date. It includes cybersecurity and anti-tampering protection requirements, such as:
- Strong authentication and authorisation mechanisms
- Secure firmware updates
- Tamper detection and prevention measures
Fines for Non-Compliance
The UK smart charging regulations impose fines for non-compliance as follows:
- £10,000 for each relevant charge point in respect of which there has been a breach of the obligations in respect of the sale of charge points (Regulation 4)
- £250,000 for a breach of the provisions relating to the obstruction of the enforcement authority or the provision of false statements (Schedule 2, paragraph 8)
The enforcement authority, the Office for Product Safety & Standards (OPSS), can serve a Civil Penalty Notice requiring payment of a financial penalty regarding a breach of any of the regulations. The OPSS website states that their approach will be risk-based and proportionate. They will work with businesses to help them comply with the regulations but will not hesitate to take enforcement action against businesses found in breach.
Approved Charger List and OZEV Grants Eligibility
The Office for Zero Emission Vehicles publishes a list of chargepoint models authorized for residential and commercial properties. However, whether a chargepoint manufacturer accepted for enforcement undertaking for smart charging regulations non-compliance can use OZEV grants depends on the specific terms of the enforcement undertaking. The OZEV website states that “if a chargepoint manufacturer has been accepted for an enforcement undertaking by OPSS, then their chargepoints may be eligible for the grant scheme, subject to certain conditions”.
The specific conditions required for a chargepoint manufacturer to be eligible for the grant scheme, if accepted for an enforcement undertaking, are not publicly disclosed. However, it is likely that the manufacturer will need to demonstrate that they have addressed the non-compliance and are committed to complying with the regulations in the future. For clarification on eligibility, you should contact OZEV directly.
How Wevo Ensures Compliance for Every Eligible OCPP Charger
A charge point management system (CPMS) can be vital in ensuring compliance with UK smart charging regulations by providing a centralised platform for managing and monitoring charge points. Here are some specific examples of how the Wevo Energy CPMS can ensure compliance:
-
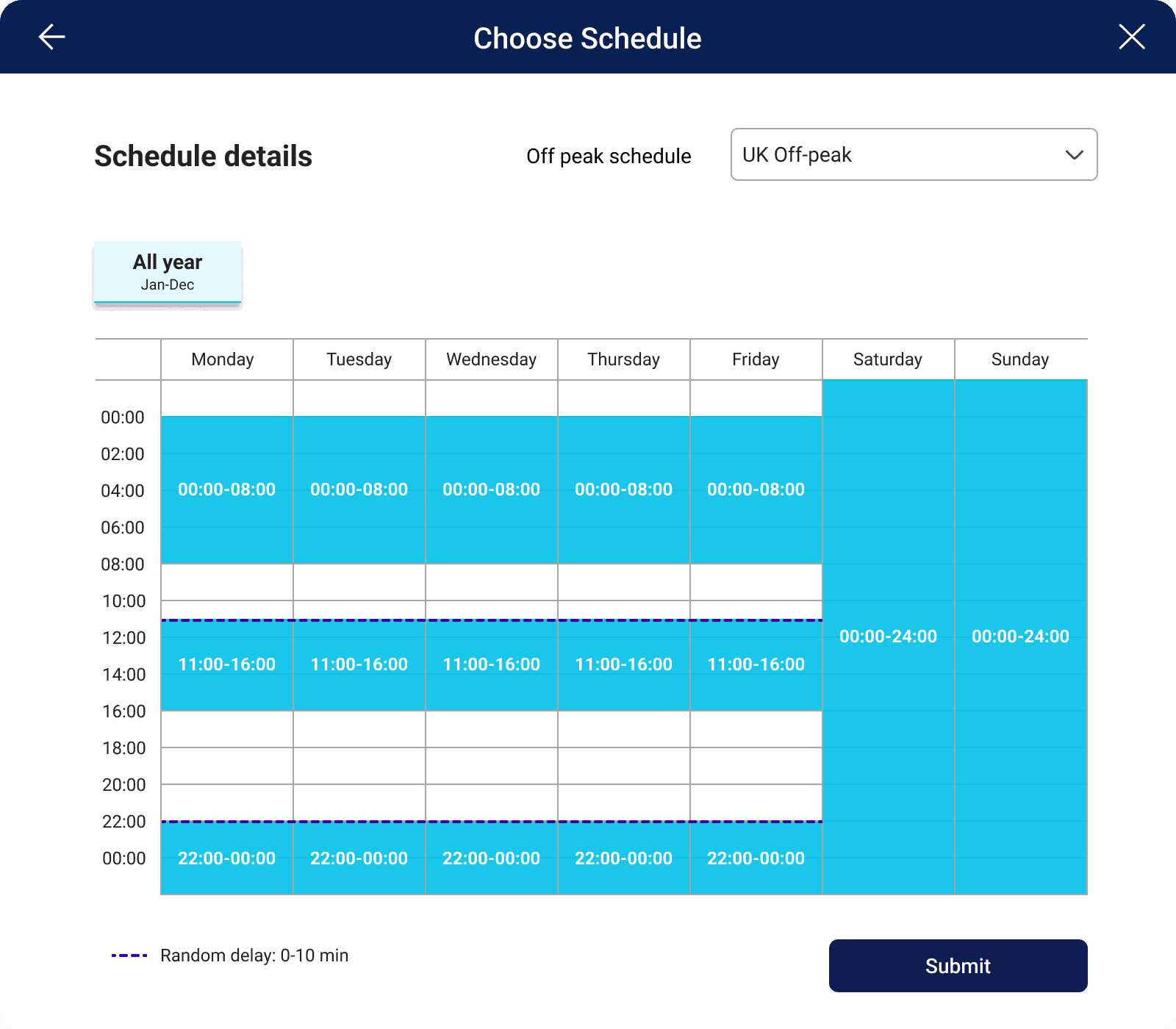
Set default charging schedules:
The Wevo platform sets default charging schedules for all charge points, thereby ensuring compliance by charging vehicles during off-peak hours when electricity is cheaper and there is less demand on the grid.
-
Enable randomised delays:
The Wevo platform enables randomised delays for all charge points. This helps to spread out the load on the grid and prevent overloading during peak hours. The Wevo platform implements a random start time between 0 and 10 minutes, in accordance with the regulations.
-
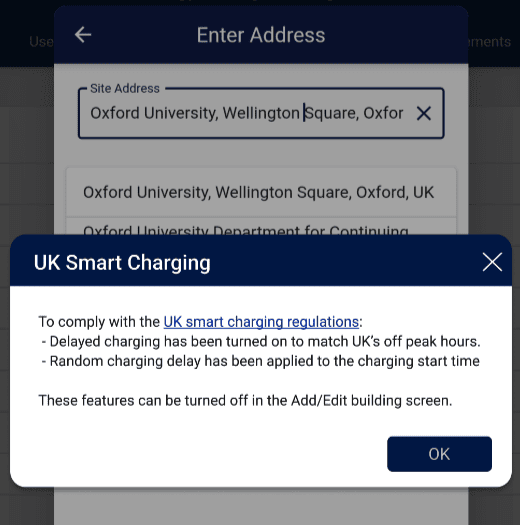
Ensure proper defaults are set:
According to the UK smart charging regulations, having scheduling and randomisation capabilities is not enough. These settings must be used as defaults for every new charger installed. The Wevo platform detects any charger installed at a UK address and sets the defaults accordingly, although administrators can override them manually later.
-
Implement cybersecurity measures:
The Wevo platform enforces cybersecurity measures for all charge points, such as strong authentication and authorisation mechanisms, secure firmware updates, and tamper detection and prevention measures. It is one of the few systems globally to be fully certified for OCPP Security. The platform ensures every connected charger is strongly encrypted and authenticated, provides secure firmware upgrades, and notifies administrators if the charger has been tampered with.

-
Collect and analyse data on energy consumption and charging patterns:
The Wevo platform collects and analyses data on energy consumption and charging patterns. This data can identify opportunities to reduce energy costs and improve the efficiency of charging operations.
-
Provide remote access to charge points:
The Wevo platform provides remote access to all charge points, allowing businesses to manage and monitor charge points from a central location, even if the charge points are distributed across multiple sites.
-
Send and receive signals from charge points:
The Wevo platform sends and receives signals from all charge points, allowing businesses to participate in DSR programs, which can help manage electricity demand and reduce costs.
Summary
Complying with the UK smart charging regulations is crucial for every charger manufacturer, charge point operator (CPO), installer, and owner, as failing to comply can result in heavy fines. Choosing the right hardware and management software is key to compliance. The Wevo Energy OCPP-certified platform is hardware agnostic and can ensure compliance with any standard hardware solution. Contact us to learn more.


