EV Roaming Overview
EV roaming with OCPI allows a driver to charge at multiple networks using a single RFID or application. Roaming is critical to the wide-scale success of EV adoption. It is similar to the evolution of mobile telephony, where, historically, each user could only make calls on their home network. Over time, users could roam to other networks, and today, national and European regulations mandate roaming at flat prices.
The most prominent protocol for EV roaming is the Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI), which is maintained and endorsed by the EVRoaming Foundation. OCPI supports connections between eMobility Service Providers (eMSPs) with EV drivers as customers and Charge Point Operators (CPOs) who manage charge stations. This protocol is free to use and independent. It can work both bilateral as well as in combination with roaming hubs.
- Charge Point Operator (CPO) – Manages a network of chargers, including maintenance and supply of electricity. Today’s chargers can be activated using an RFID, a mobile app, or contactless credit/debit cards.
- eMobility Service provider (eMSP) – Manages a network of drivers, including providing RFIDs and a mobile app to locate chargers and holding the billing details for those drivers. Examples of eMSPs include Plugshare, Zap Map and Octopus Electric Universe in the UK, and Cellocharge in Israel.
The OCPI protocol defines the communications between CPOs and eMSPs to support token (RFID) exchange, charge point location and status, billing records, and charge point commands.
OCPI Functional Modules
OCPI provides a common language between eMSP and CPOs to support the rapid expansion of the roaming network. The OCPI protocol covers seven functional modules:
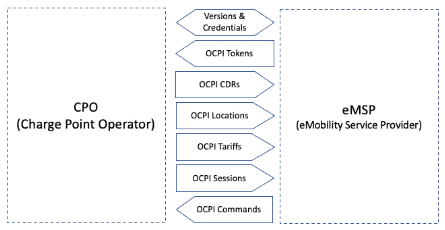
Mandatory administrative modules :
- OCPI Versions – Allow the two parties to agree on the protocol version supported by both.
- OCPI Credentials – Key exchange and authorization verification for securing the communications.
Modules used for basic RFID operations and payment processing:
- OCPI Tokens – Define the exchange of tokens (e.g. RFID details) between eMSP and CPO. The eMSP periodically sends a list of approved tokens to the CPO, which stores this list and uses it to approve charging sessions. An alternate method allows the CPO to authenticate a token in real-time.
- OCPI CDRs (Charge Detail Records) – Define the exchange of completed charge sessions for billing. When a charge session is completed, a record is created containing the details of the transaction (cost, duration, energy, etc.) and sent to the eMSP for payment.
Modules used by the eMSP for creating an interactive charge point map:
- OCPI Locations – Define the exchange of charging locations data, including charge point capabilities, availability, and cost. The CPO periodically sends this list to the eMSP, which uses it to provide a live charge map.
- OCPI Tariffs – Used in conjunction with OCPI Locations to provide details of the tariff that applies to a specific charge point.
Modules used by the eMSP for app charging initiation and app status updates:
- OCPI Sessions – Defile the exchange of interactive session data, including charging speed, energy used so far, and socket status (charging, complete, etc.) The eMSP can use this data to update the mobile app with the charging status.
- OCPI Commands – Allows the eMSP to send charging commands to a specific charger. Commands include Reserving a charger, starting or stopping a session, and unlocking a stuck connector. The eMSP can use these commands to implement in-app charging initiation.
Bilateral OCPI vs. roaming hubs
By default, OCPI supports the bilateral connectivity of one CPO to one eMSP. For multiple CPOs and eMSPs, a fully connected mesh would need to be created, connecting every pair. Although this would work for a small set of entities, it would become impractical for larger networks. This is when roaming hubs such as Hubject, GIREVE, or e-clearing.net make sense.
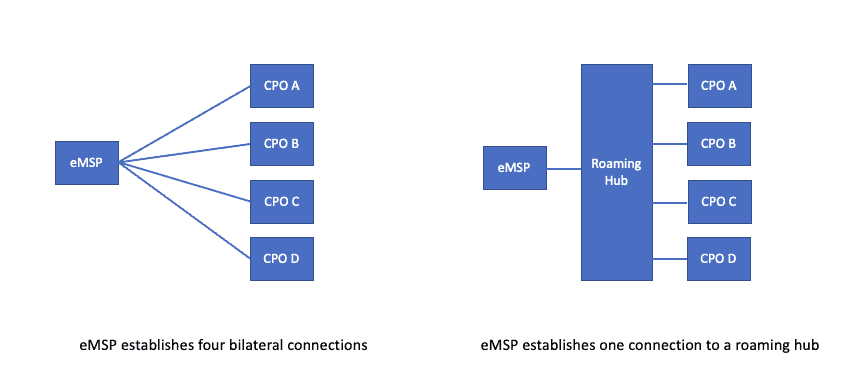
The roaming hubs provide easier integration and simplify commercial negotiations, but they come at an extra cost, which the roaming hub adds on top of the CPO pricing.