The complexity of EV charging protocols, whose acronyms mostly contain the letters P and O, can be very confusing for most people. Fear not, as the experts of Wevo Energy are here to help clarify these and explain exactly what OCPP, OCPI, and OSCP are, along with the importance of EV charging protocol standards in the industry.
It all starts with managing the charger
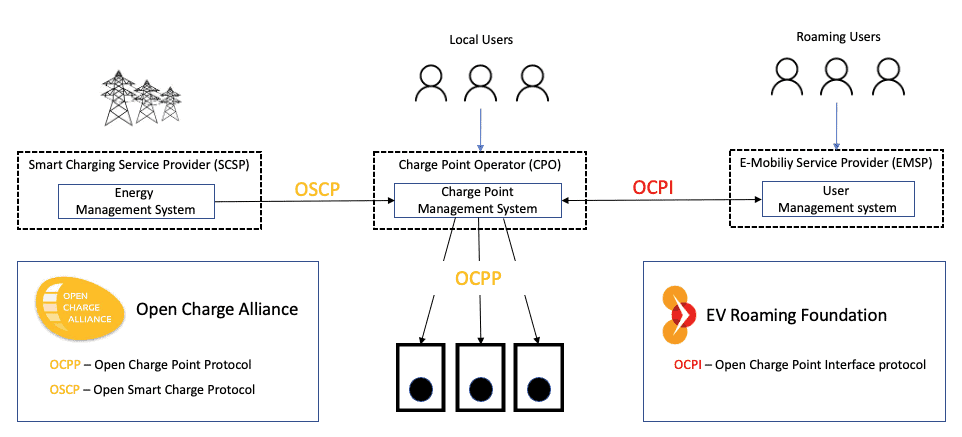
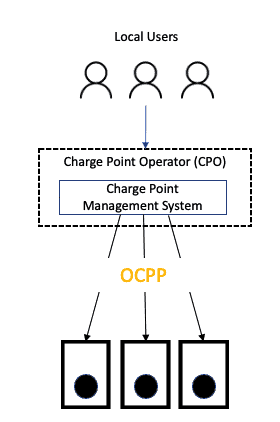
The Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP), developed by the Open Charge Alliance, is designed for controlling and managing charging stations from a central system. It enables two-way communication between chargers and the back-end https://sajs.ntt.edu.vn/ Charge Point Management System (CPMS) that controls them. OCPP supports many different functions, such as authentication, authorization, start/stop charging, and billing. It is very secure and relatively easy to implement. Using OCPP, a Charge Point Operator (CPO) can install chargers, sign up users, and enable charging with an App, RFID card, or QR codes. Most public charging networks operate this way.
The Walled Garden Dilemma
As more EVs took to the road, more Charge Point Operators (CPOs) joined the party and started their own network using their own OCPP server and their own RFID. The UK alone has over 50 such slot88 resmi networks listed on ZapMap. Since OCPP was designed to manage a https://www.meridianpint.com/touchless-menu/ single network, it quickly became a problem for users of one network to use other networks. In fact, most drivers have to register to multiple networks, carry multiple RFIDs, and download multiple mobile apps. What a mess…

Typical drivers must carry multiple RFID cards, as many charging networks do not support roaming.
eMobility Service Providers (eMSP) to the rescue
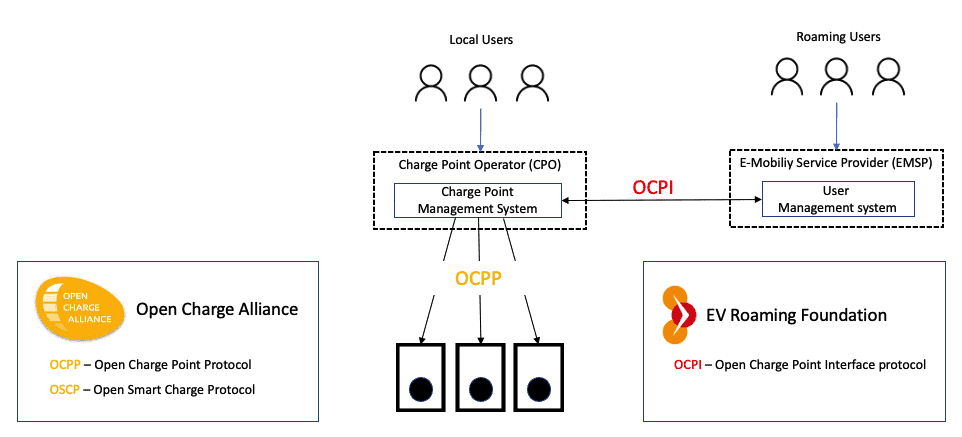
As driver pain became evident, new entities started to appear. Welcome the eMobility Service Provider (eMSP). The eMSP serves EV drivers by providing them with consolidated access to many charging networks. Drivers get a single eMSP RFID and a single app and can use them across many charging providers. Welcome Roaming!
Examples of eMSPs include Plugshare, Zap Map and Octopus Electric Universe in the UK, and Cellocharge in Israel. Some large EV fleets even created their own eMSP to allow their drivers to charge at public networks.
This wonderful roaming capability is enabled by the Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI) protocol, which is maintained and endorsed by the EVRoaming Foundation. It enables operators to offer services across multiple networks, giving users more charging options. The OCPI protocol defines the communications between CPOs and eMSPs. It enables token (RFID) exchange, charge point location and status, billing records, and charge point commands. The full details of this protocol are beyond our scope, but here is a good overview of OCPI.
Controlling site power
With so many charge points often installed in densely populated areas with limited electric grid capacity, grid operators are becoming concerned. On Aug 31, 2022, the California Grid System Operator sent a Flex Alert asking all residents to voluntarily reduce their electricity use between 4 p.m. and 9 p.m. With the number of new EV registrations on the rise, more such cases are expected.
OSCP (Open Smart Charging Protocol) is an open communication protocol, also developed by the Open Charge Alliance. It is a protocol between a charge point management system (CPMS) and a smart charging service provider (SCSP). SCSPs are typically grid operators, demand response aggregators, or energy management systems. The protocol imparts a 24-hour forecast of the accessible capacity https://weddingcelebrantfrance.com/welcome/ of an electricity grid. Using this forecast, the CPMS can optimize charging times for individual vehicles and avoid exceeding the limit. OSCP sets the overall load available to the site while the Charge Point Management System distributes the available load between the chargers using dynamic load balancing.
Putting it all together
We now have a full picture of the various protocols that make up the future charging networks. Combining OCPP, OCPI, and OSCP ensures an open, secure, and reliable network that https://adspc.ad.gov.ng/ supports roaming and grid limits.